The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
One of the important laws under Marginal Utility analysis is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility.
The law of diminishing marginal utility is based on an important fact that while total wants of a person are virtually unlimited, each single want is satiable i.e., each want is capable of being satisfied. Since each wantis satiable, as a consumer consumes more and more units of a good, the intensity of his want for the good goes on decreasing and a point is reached where the consumer no longer wants it. Thus, the greater the amount of a good a consumer has, the less an additional unit is worth to him or her.
Marshall who was the exponent of the marginal utility analysis, stated the law as follows:
“The additional benefit which a person derives from a given increase in the stock of a thing diminishes with every increase in the stock that he already has.”
In other words, as a consumer increases the consumption of any one commodity keeping constant the consumption of all other commodities, the marginal utility of the variable commodity must eventually decline.
This law describes a very fundamental tendency of human nature. In simple words it says that as a consumer takes more units of a good, the extra satisfaction that he derives from an extra unit of a good goes on falling. It is to be noted that it is the marginal utility and not the total utility which declines with the increase in the consumption of a good.
Table 6 : Total and marginal utility schedule
|
Quantity
of chocolate bar consumed
|
Total utility
|
Marginal utility
|
|
1
|
30
|
30
|
|
2
|
50
|
20
|
|
3
|
65
|
15
|
|
4
|
75
|
10
|
|
5
|
83
|
8
|
|
6
|
89
|
6
|
|
7
|
93
|
4
|
|
8
|
96
|
3
|
|
9
|
98
|
2
|
|
10
|
98
|
0
|
|
11
|
94
|
–4
|
Let us illustrate the law with the help of an example. Consider Table 6, in which we have presented the total utility and marginal utility derived by a person from the chocolate bars consumed. When one chocolate bar is consumed, the total utility derived by the person is 30 utils (unit of utility) and the marginal utility derived is also 30 utils. With the consumption of 2nd chocolate bar, the total utility rises to 50 but marginal utility falls to 20. We see that till the consumption of chocolate bars increases to 9, the marginal utility from the additional chocolate bars goes on diminishing (i.e., the total utility goes on increasing at a diminishing rate). The 10th chocolate bar adds no utility and therefore, the total utility remains the same at 98. However, when the chocolate bars consumed increases to 11, instead of giving positive marginal utility, the eleventh chocolate bar gives negative marginal utility or disutility as it may cause him discomfort.
From Table 6, we can conclude the following important relationships between total utility and marginal utility
1. Total utility rises as long as MU is positive, but at a diminishing rate because MU is diminishing.
2. Marginal utility diminishes throughout.
3. When marginal utility is zero, total utility is maximum. It is a saturation point.
4. When marginal utility is negative, total utility is diminishing.
5.MU is the rate of change of TU or the slope of TU.
6. MU can be positive ,zero or negative.
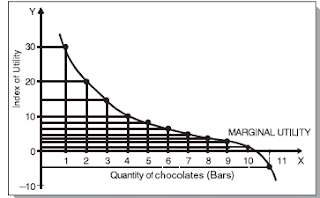
Graphically we can represent the relationship between total utility and marginal utility (fig. 11).
Fig. 11 : Marginal utility of chocolates consumed
As will be seen from the figure, the marginal utility curve goes on declining throughout. The diminishing marginal utility curve applies to almost all commodities. A few exceptions however, have been pointed out by some economists. According to them, this law does not apply to money, music and hobbies. While this may be true in initial stages, beyond a certain limit these will also be subjected to diminishing utility.
The Law of diminishing marginal utility helps us to understand how a consumer reaches equilibrium in case of a single good. It states that as the quantity of a good with the consumer increases, marginal utility of the good decreases. In other words, the marginal utility curve is downward sloping. Now, a consumer will go on buying a good till the marginal utility of the good becomes equal to the market price. In other words, the consumer will be in equilibrium (will be deriving maximum satisfaction) in respect of the quantity of the good when marginal utility of the good is equal to its price. Here his satisfaction will be maximum.
What happens when there is a change in the price of the good? The equality between marginal utility and price is disturbed when the price of the good falls. The consumer will consume more of the good so as to restore the equality between the marginal utility and price. The marginal utility from the good will fall when he consumes more of the good. He will continue consuming more till the marginal utility becomes equal to the new lower price. On the other hand, when price of the good increases, he will buy less so as to equate the marginal utility to the higher price. We can say that the downward sloping demand curve is directly derived from the marginal utility curve.
In reality, a consumer spends his income on more than one good. In such cases, consumer equilibrium is explained with the law of Equi-Marginal utility. According to this, the consumer will be in equilibrium when he is spending his money on goods and services in such a way that the marginal utility of each good is proportional to its price and the last rupee spent on each commodity yields him equal marginal utility.
The law states that the consumer is said to be at equilibrium, when the following condition is met:
(MUX/PX) = (MUY/PY) or (MUx/ MUY) = (Px/PY)
Goods and Service Tax Book (Updated upto 20th January 2018)
GST Student friendly Book most relevant/Useful for CA Intermediate/IPCC, CS executive , CWA Intermediate and CA final.
Also useful for B.Com / M.Com / MBA/ BBA/UPSC/ SSC and Various Govt Exams.!!
This book is approved by Ministry of HRD Govt.of India as Students friendly book.
Click on link given to Purchase Book- https://goo.gl/ArNFJx
Author Name- CA Harshita Raichandani and CA Dhananjay Ojha
Unique features of This GST Book.
1.80+ GST chart included for quick revision of chapter.
2.Provisions presented in this book in simple manner.
3.Bullet and Heading given for Long term memorisation.
4.Updated upto 25th GST council recommendation {18th January, 2018}.
5.70+ Value added questions given with answer.
6.16 Chapters fully Coverage given.
7.Definitions of Technical term related with GST is given at one place.
8.Most useful for CA Intermediate/IPCC, CS executive , CWA Intermediate and CA final. ALSO useful for B.Com / M.Com / MBA/ BBA/UPSC/ SSC and Various Govt Exams.
Click on below Link to purchase Student friendly GST Book.
http://www.comgurukul.com/educational-books/gst-book/
GST (Goods and Services Tax) Book -A student friendly Book. - Bharat Gurukul
GST Student friendly Book most relevant/Useful for CA Intermediate/IPCC, CS executive , CWA

No comments:
Post a Comment